What is interventional cardiology?
Escrito por:Interventional cardiology is a non-surgical option to treat a variety of heart problems. We spoke to Dr Kare Tang, a renowned consultant cardiologist based in London, Colchester and Basildon who has extensive experience in interventional cardiology, about this branch of medicine to understand more about the conditions it can treat and how effective it is.
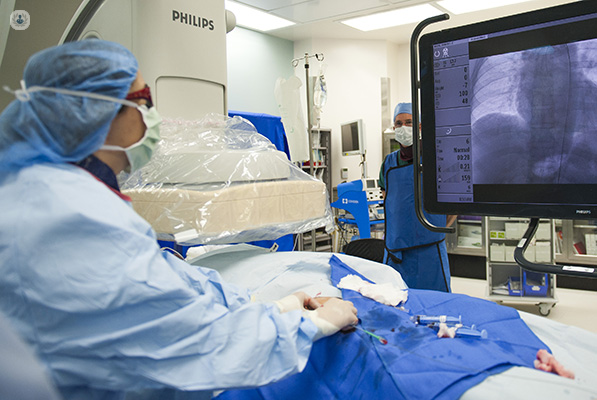
What does interventional cardiology involve?
Interventional cardiology is a subspecialty of cardiology that deals specifically with the catheter-based treatment of structural heart diseases. Most of the procedures are carried out in the cardiovascular system, which includes your veins, heart and arteries. This subspecialty of cardiology takes a minimally invasive approach to treatment, by a needle puncture of a few millimetres in size and doesn’t require large cuts or instruments entering the body.
What conditions does interventional cardiology treat?
It primarily includes the treatment of coronary artery disease, vascular disease and acquired structural heart disease. It assesses and treats coronary artery disease when a clinician suspects it is causing ischaemic heart disease - a term given to heart problems causing narrowed arteries. This also includes the spectrum of conditions ranging from stable angina to heart attacks.
Treatment involves non-surgical procedures using balloons and stents and carrying out minimally invasive investigations of the coronary artery using pressure wires (iFR/FFR) and imaging tools such as intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherent tomography (OCT). All of these treatments are carried out via a catheter introduced into an artery in the wrist or groin under local anaesthetic.
How are patients prepared for a procedure?
Patients typically attend as an outpatient or in some cases, may need to stay overnight in the hospital. Before a procedure, the patient is advised to take aspirin and clopidogrel medications. Other blood-thinning medication or metformin for diabetes is typically omitted 1-2 days prior. Blood tests, kidney function tests and a complete blood count will be needed as the dye used in the treatment can affect the function of the kidneys. Normally, the patient only needs to abstain from eating or drinking 2 hours before the procedure as it is carried out under local anaesthetic.
How effective is interventional cardiology?
Interventional cardiology is primarily known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), where specialists use metallic stents or drug-coated balloons to treat coronary narrowings or blockages. They are highly effective in eliminating angina symptoms and improving the patient’s heart function. Overall, interventional cardiology is very safe and has a low complication rate at around 1%.
What does aftercare involve?
Recovery is relatively simple. There is usually a small needle puncture wound in the wrist if the specialist accessed through the radial artery route. Plastic bandages are applied for compression and need to be worn for 2-3 hours after the procedure to stop any bleeding from the high-pressure artery. If the procedure was carried out from the groin femoral artery route, the puncture hole is usually sealed with a collagen plug known as an Angio-Seal which takes around 3 months to dissolve.
What is the alternative to interventional cardiology?
The alternative to PCI treatment is to either take regular medication for symptomatic control or if the disease is significant, then the specialist and patient may want to consider coronary artery bypass surgery. This involves redirecting your blood around a section of a partially or fully blocked artery in your heart, using a healthy blood vessel taken from your arm, chest or leg. It is a major operation carried out under general anaesthetic and the recovery time is much longer.
If you would like to make an appointment see Dr Kare Tang, visit his Top Doctors profile and check his availability.


