Fracture fixation: resetting the bone
Autore:Fractures are a nasty business and getting the bone reset is crucial to recovery. But did you know there are a number of ways to do this? Experienced orthopaedic surgeon Mr Peter Peev explains fracture fixation and why these techniques are needed.
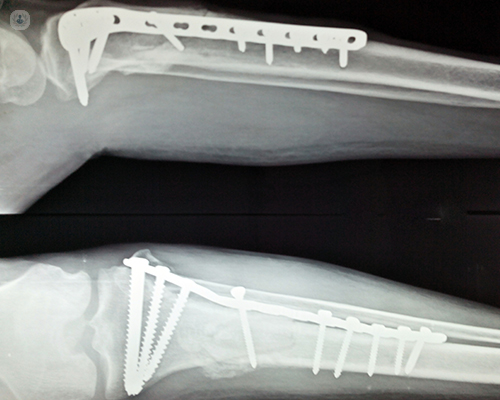
What is fracture fixation and when is it required?
Fracture fixation is a method of stabilising a broken bone using a variety of medical devices. Separated bone fragments are aligned and connected together with an implant. This eliminates movements between bone fragments and allows the fracture to heal in the desired position. It is an alternative form of stabilisation to a plaster cast, splint or strapping.
The advantage of fracture fixation is that it allows early mobilisation of the injured limb and prevents deformities. It is required when the displacement of the broken bone is significant and correction and stabilisation cannot be achieved with other methods. It is often the preferred method of treating long bone fractures, fractures extending into adjacent joints, or for patients with multiple injuries.
What’s the difference between internal and external fixation?
The difference between internal and external fixation is in the type of device used for fixation. Internal fixation is performed by using implantable devices. These are usually screws, plates or long metal rods, called intramedullary nails, pins or wires.
With external fixation, the surgeon will use a device called an external fixator. This is a modular system of pins, rods and clamps. The main bone fragments are held with pins inserted through the skin and stabilisation is achieved by connecting the pins to rods, bypassing the fracture. The rods remain outside the extremity, hence “external” fixation. It can be used temporarily if the condition of the limb doesn’t allow the use of internal devices, or as a definitive treatment alone.
What methods are used to perform the bone reset?
The process to reset a broken bone is called a fracture reduction. It is aimed at restoring the normal anatomical position of the displaced fragments. It may include elevation of impacted joint surface fragments when a joint is involved in a fracture. When there is no joint involvement, fracture reduction restores correct length, alignment and rotation of the broken bone.
Fracture reduction is achieved via closed or opened techniques or a combination of both. Closed (indirect) reduction applies traction to the broken limb along its anatomical axis. This can be done by the surgeons or using a device and X-rays are taken to monitor the reduction.
Open (direct) reduction exposes the fracture site with an incision so that the surgeon can see the fragments as he restores them to their anatomical position. X-rays are also obtained to confirm the reduction.
What are the fixators made of?
The devices used for fracture fixation need to provide strong and rigid support to the broken bone until it heals. Healing usually takes several months. They have to sustain the weight-bearing and bending forces during movement. The materials they are made of should have the least side-effects and show high biocompatibility, osseointegration properties, and corrosion resistance.
Stainless steel is considered to be one of the most suitable metals for manufacturing implants for internal fixation devices owing to its favourable combination of mechanical properties and biocompatibility. In recent years, more devices have been developed from titanium and titanium alloys. Titanium has been shown in research to have excellent biocompatibility and non-sensitisation for tissues.
How do I know which method is the correct one for me?
Your surgeon will advise you on the best method of fixation. This will depend mainly on the type of injury, which bone is affected, the degree of displacement, and associated injuries. The greatest advantages of using internal fixation are:
- Better reduction
- Stronger stabilisation
- Earlier mobilisation
In many cases of internal fixation, no plaster will be required, which reduces the chances of developing joint stiffness and muscle weakness during treatment. Using a cast requires a longer period of immobilization and frequents X-rays to monitor the position of the fracture.
When would I need them removed?
External fixators are always removed at some stage of treatment. This may be the time when the final method can be applied or when the fracture is healed. Internal fixation devices can remain in the body forever. The primary plan is usually not to remove the implants. They do not cause any harm to the body.
There will be certain circumstances when removal may be required:
- An infection that cannot be cured with antibiotics
- Implant failure – metal implants can break
- When the fracture is healed, if the implant is too prominent under the skin and causing discomfort or irritation
In most cases, implanted devices do not require routine removal.
Are there any risks associated with fracture fixation?
Fracture fixation is a surgical procedure. Any surgical procedure is associated with certain risks. These are:
- Infection
- Blood clots (in the case of lower limb injuries)
- Nerve injuries
These can usually be managed by administering antibiotics or blood-thinning medication before and after the surgical procedure. Chances for complications are also dependant on the severity of the injury and existing other comorbidities. This is usually all considered and discussed with the patient well in advance, presenting the balance between risks and advantages. Overall, fracture fixation has proven to be a very safe and successful procedure and is widely performed in clinical practice.
Visit Mr Peev’s Top Doctors profile to book an appointment.


