I have fibroids – what are my treatment options?
Autore:Do you suffer from fibroids? The chances are that you do, or you will as up to 40% of women aged 35 or older have fibroids. Fibroids can either be symptomless or can cause numerous menstrual problems, including heavy bleeding. Choosing your treatment can be overwhelming, but Dr Paul Crowe, a leading interventional radiologist with lots of experience in treating uterine fibroids lays out the A to Z in treatment options for this common condition.
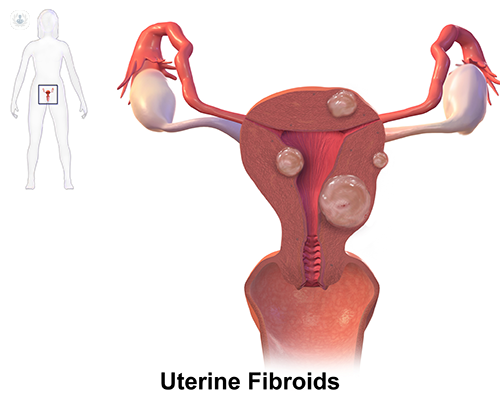
Fibroids – what are they?
Fibroids are abnormal growths found on the muscle walls of the womb or uterus. Also known as uterine fibroids, these are the most common tumours found in the female genital tract. Although tumours, they are benign growths (non-cancerous) and do not always produce symptoms. However, when fibroids do cause symptoms, women can experience very heavy or painful periods.
Are fibroids common?
Uterine fibroids are very common, with those suffering from fibroids increasing in numbers with age until menopause. Around 20% to 40% of women aged 35 or older have uterine fibroids. They are also more common in some ethnic groups.
How can fibroids be treated?
Your specialist will discuss the different treatment options available with you, as the course of treatment chosen is unique to your circumstances.
Combination treatments:
- often you will follow a combination of different treatments, particularly if you have different types of fibroid
- for example, you might have embolisation, followed by medication or embolisation followed by surgery
Endometrial ablation:
- this treats the uterine lining to reduce heavy menstrual bleeding (menorrhagia) made worse by fibroids
Hysterectomy:
- either the whole uterus and cervix are removed, or the cervix and ovaries are left intact (subtotal hysterectomy)
- this is more invasive, and usually recommended to women who have severe bleeding problems caused by their fibroids
- recovery time is much longer
Medical treatment:
- tablets or injections that manipulate hormones that affect fibroid growth can be taken
- fibroids can return if this treatment method is discontinued
Myomectomy:
- a surgical procedure that removes the fibroids
- this procedure can be carried out hysteroscopically (through the cervix), laparoscopically (keyhole surgery) or as open surgery
MRI guided focused ultrasound (MRgFUS):
- high intensity ultrasound waves onto the fibroids in an MRI scanner heat treats the and destroys them
- this option is only appropriate in cases where the location and size of the fibroids is optimal
Uterine artery embolisation (UAE):
- also known as uterine fibroid embolisation (UFE)
- a mainstream treatment option that shrinks the fibroids by blocking their blood supply
How to choose your treatment?
After in-depth discussions and on the basis of your diagnosis, a gynaecologist and interventional radiologist will recommend the best course of action for the treatment of your fibroids. However, it is also best to research the options ahead of your appointment, so that you can ask as many informed questions as possible.
If you require fibroid treatment or would like to find out more, make an appointment with a specialist.


