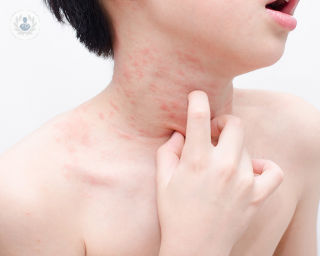
Allergic urticaria
What is allergic urticaria?
Allergic urticaria is a skin disease that shows up as a skin rash (white or red hives) and itchiness across the body. It tends to be more common than cases of non-allergic urticaria, where symptoms tend to disappear within a few hours, as there is an allergen triggering it.
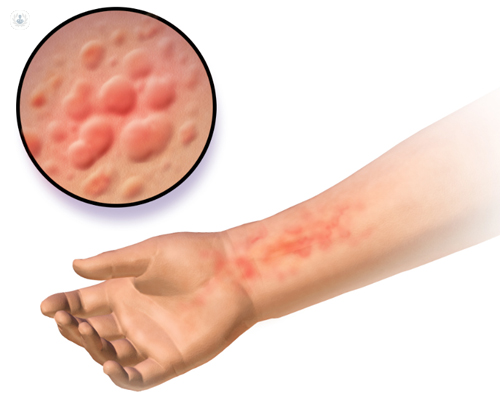
What is the prognosis of allergic urticaria?
Urticaria or hives can be a bothersome condition, although in most cases it is harmless. In contrast with chronic urticaria, which can last for months or even years, the symptoms of allergic urticaria disappear within a few days. Nonetheless, it is advisable to see an allergist in order to get a proper diagnosis.
What are the main symptoms?
Urticaria symptoms tend to include itching and swelling or inflammation of the skin surface, as well as an outbreak of red welts with defined edges. These welts tend to appear and disappear, and can sometimes even spread and create a raised skin area.
How is allergic urticaria detected?
Hives can normally be diagnosed by a specialist just by looking at them. Sometimes it may be necessary to take a biopsy and blood test in order to confirm an allergic reaction and to know the reason for the urticaria.
What causes it?
When there is an allergic reaction, the body releases histamines and other chemicals that cause itchiness, swelling, and other symptoms. Some substances that could trigger hives to break out include:
- animal hair
- insect bites or stings
- medications
- pollen
- foods, especially seafood and fish, although it is also quite common to have a reaction with nuts, eggs, and milk.
Other things that could cause an outbreak are emotional stress, extreme exposure to heat or cold, a variety of diseases and infections, and exposure to water among others.
How can it be prevented?
In order to prevent hives breaking out, it is important to have allergy tests done to identify what substances may cause an allergic reaction. It is recommended that exposure to these substances is avoided in order to not have an outbreak of urticaria.
How is allergic urticaria treated?
In some cases, treatment is not necessary as the reaction has gone away on its own. However, treatment normally involves antihistamines and corticosteroids administered under medical supervision. Patients are advised to avoid hot showers on the affected area and to not wear tight clothing, as this can cause irritation.
In cases where the allergic reaction is severe, epinephrine (adrenaline) or steroids may be injected.
Which specialist treats allergic urticaria?
An allergist is the specialist who can diagnose and treat allergic reactions and the underlying allergy involved.
When is allergic urticaria considered a medical emergency?
It is considered to be a medical emergency when skin rashes are found by a doctor or noticed by a patient in the throat, tongue, and/or lungs. If allergic urticaria is found in these parts of the body, the patient will likely experience difficulty breathing, which is considered to be a medical emergency.
What underlying conditions might allergic urticaria be a sign of?
Thyroid disease, hepatitis, lupus, vasculitis, as well as urinary tract infections are all underlying conditions that usually lead to allergic urticaria.