Burns
Tania Cubison - Plastic surgery
Created on: 11-13-2012
Updated on: 09-28-2023
Edited by: Lauren Dempsey
What are burns?
Burns are injuries to the skin and other tissues of the body that can happen to anyone. They develop following contact or exposure to agents such as the sun, heat, electricity, radiation, certain chemicals, or objects and other substances of a high temperature. Burns can be mild to very severe, causing symptoms that range from mild discomfort to excruciating pain.
Scalds are similar to burns but rather than being caused by dry heat, they are caused by something wet and hot, like boiling liquid or steam.
If you have suffered a burn, you should seek medical help immediately at first. Depending on the nature of the burn, you may need to seek the help of a specialist dermatologist or plastic surgeon after the initial treatment of the burn.
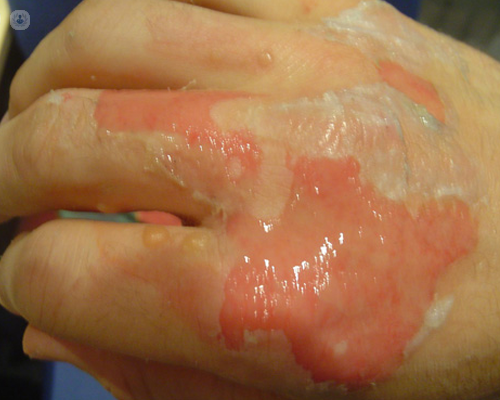
What are the different types of burns?
There are two ways to distinguish burns, firstly by their severity.
-
First-degree burns
Only the outer layer of the skin is damaged. -
Second-degree burns
In this type of burn, both the outer layer of the skin and the layer beneath it are damaged. -
Third-degree burns
The most dangerous for your health since they damage the deepest layers of the skin and even the tissues that are underneath.
Burns can also be classified according to the extent of the body they have affected: minor burns are those that have reached less than 10% of the total surface of the body, whilst moderate burns can reach up to 20% of the total surface and anything more than 20% is considered a major burn.
What are the causes of burns?
The most common causes of burns are:
- Sun exposure.
- Heat: either in the form of fire (flames), objects at high temperature, cooking liquids, cooked foods that are still hot, or steam.
- Cold: extreme cold elements such as ice or liquid nitrogen also cause burns.
- Chemicals: burns of chemical origin are caused by contact or intake of abrasive chemicals, like bleach.
- Electricity: by contact with unprotected cables or by putting your fingers or objects in an electrical socket.
- Radiation: from an X-ray, UV-ray, or radiation cancer therapy.
What are the common symptoms of burns?
The main symptoms of burns include:
- reddening of the skin or, in more serious cases, white or charred skin
- blisters
- peeling skin
- pain and burning
- inflammation
In the case of respiratory tract burns symptoms may include:
- cough
- difficulty breathing
- wheezing
- dark mucus or black spots in the mucus
- changes in voice
What complications can arise from burns?
Burns can sometimes lead to further complications, such as:
- infections, potentially sepsis
- hypovolemia (fluid loss) and dehydration
- hypothermia
- breathing issues
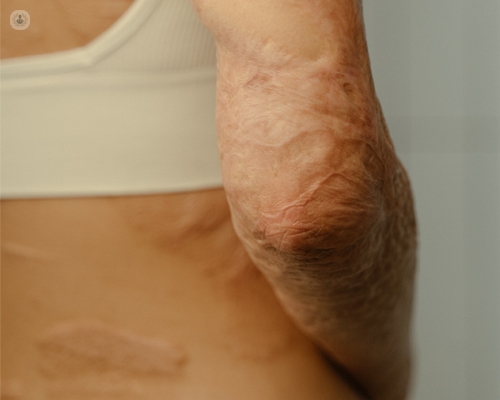
- scars
- arrhythmia
Can burns be prevented?
There are different methods to protect the skin and prevent it from sunburn. Sunscreen can be applied in the form of creams, gels, and sprays, as well as lip balms with sun protection. It is also recommended to avoid sun exposure in the hours of peak sun intensity, around midday. Covering yourself with a hat or clothing also prevents sunburn.
Of course, it is essential to avoid fires and contact with fire or high-temperature elements such as irons, frying pans, ovens, or vitroceramic hobs. Take care to protect yourselves and others in everyday life, for example in the home, to prevent avoidable burns. Avoid direct contact with highly flammable substances or abrasive chemical products by using protective clothing.
When should you seek medical attention for a burn?
First-degree burns and second-degree burns, like sunburn and minor scalds, can usually be dealt with at home. Otherwise, immediately seek help if:
- A large area of the body is burnt.
- The burn is deep.
- The skin appears leathery or charred as a result.
- The burn is chemical or electrical.
- You have trouble breathing.
You may need to visit a doctor at a later date if:
- The burn becomes infected.
- There is little to no healing for an extended period (two weeks).
- Severe scarring.
How are burns diagnosed?
The diagnostic examination of burns usually begins with a physical examination by a dermatologist, who will assess the extent of the affected skin and the severity of the burn. Depending on the symptoms of the patient and the severity of the burn, the specialist may also require tests, such as X-rays or other imaging tests, to detect whether the internal structures of the patient have been affected.
What specialist treats burns?
Dermatologists are responsible for detecting burns and prescribing their treatment. In case the patient requires surgery, they will go to a specialist in plastic and reconstructive surgery.
How are burns treated?
The treatment for burns will depend on the type of burn and degree of severity. Smaller burns can be treated with aloe vera and specific creams.
In more serious burns the treatment may include medications, bandages, and physiotherapy, all of which aim to eliminate the pain, prevent or cure infections, remove dead tissue, reduce the appearance of scars, and recover normal functions.
The purpose of burn surgery is to treat and restore both the appearance of the tissues affected by this type of injury and the recovery of its functionality, in cases of major burns. Depending on the depth and the cause of the burn, as well as the location of the scars, different treatments or interventions will be required to repair the injuries caused in the tissues and structures or the organs affected.
Currently, techniques of natural cell regeneration and skin graft implantation are applied, in cases where the tissue that has been destroyed by a burn can’t regenerate by itself. To do this, thanks to the advances of plastic surgery in this field, cells of the skin are cultivated that allow the creation of skin grafts that can reconstruct this type of injury when they are very serious, obtaining safer and more satisfactory results to heal burns.
What can make burns worse?
When treating a burn at home, be aware that some home remedies can make burns worse. Ice or ice-cold water can often cause further damage to the skin or affected area by reducing blood flow. Other home remedies which should be avoided include treating the burn with butter, egg whites, or toothpaste.
When should you cover a burn?
If you are sunburnt, keep the area covered with light, cotton clothing and wear a hat. Factor 50 suncream should be used. For minor burns, you might not need to cover them. However, for more serious burns or to prevent infection, you may cover it with a non-stick bandage.
What is the prognosis for burns?
Burns can be very severe, and become potentially life-threatening. The consequences of burns will depend on the agent that caused it and the degree of injury. Burns are especially dangerous in babies, children up to 4 years old, and the elderly since their skin is usually thinner.
The damage caused by skin burns is cumulative. For example, sunburn can lead to skin cancer. In many cases, the development of skin cancer appears during adulthood, as a result of lifelong accumulated skin damage caused by sunburn.

