Rosacea
What is rosacea?
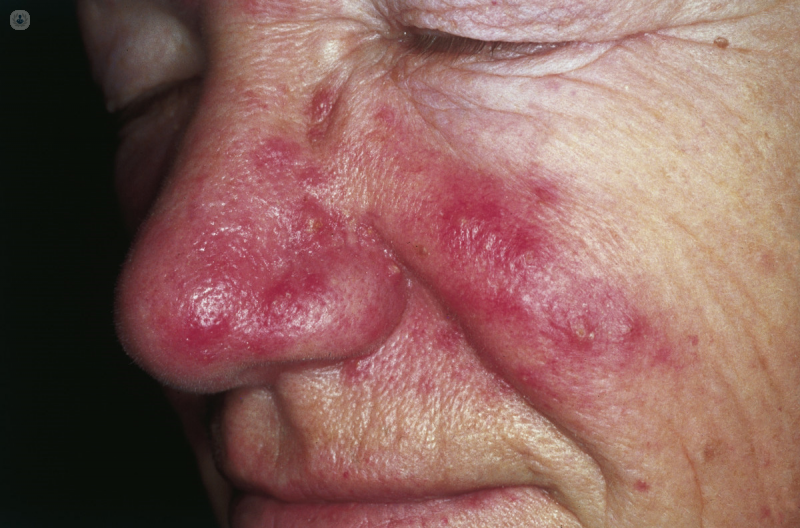
Rosacea is a chronic skin condition that causes a facial rash, which may include red blotches, telangiectasia (spider veins), pimples or spots, and possibly a burning sensation on the skin of the cheeks, nose, chin and forehead. It is a long-term condition that appears more frequently in middle-aged people and can vary in intensity.
What are the symptoms of rosacea?
Rosacea can manifest as several symptoms, including:
- Redness of the face (often giving the appearance of blushing)
- Bumps or pimples on the skin
- Patches of rough, dry skin
- Swelling, particularly around the nose and eyes (a bulbous red nose is a common indicator of severe rosacea)
- A burning or stinging sensation
- Telangiectasia (spider veins – thin and reddish lines form under the skin because the blood vessels under the skin are enlarged.
- Eye problems, including itching, dryness, swelling, light-sensitivity, bloodshot or watery appearance, etc.
Different patients may experience a different selection of symptoms, the most common being the unexplained redness of the face, which often bears a resemblance to acne (although the two are distinct conditions).
Rosacea tends to flare up in cycles, with patients suffering symptoms for a period of weeks or months, before the symptoms disappear for a similar period.
What are the causes of rosacea?
The cause of rosacea is unknown but there are several factors that are thought to contribute to or worsen it. For example excessive consumption of alcohol, caffeine or hot and spicy food is thought to trigger episodes, as can intense physical activity. Other factors include:
- Age – rosacea occurs most commonly in people between 30 and 50 years of age.
- Skin type – fair-skinned people seem to be more susceptible (especially those with blond hair and blue eyes).
- Genetics – family history of the condition means you are more likely to suffer from rosacea. It it also more common in people of Celtic and Scandinavian ancestry.
- Hormonal changes (for example, the menopause)
- Sudden changes in temperature
- Exposure to sun or wind
- Stress
- Some medications
- Certain bacteria like helicobacter pylori
Can rosacea be prevented?
Rosacea isn't something that can be prevented, but you can still avoid severe episodes by starting treatment as soon as possible when symptoms flare up, and keeping your skin hydrated. Other tips include:
- identifying and avoiding the things that cause a flare-up;
- avoiding products that irritate the skin, and;
- generally taking care of your skin, by using sun cream;
- make-up suited to your skin type, and;
- gentle shampoos and gels to avoid further irritation.
What is the treatment for rosacea?
Although there is no cure, the symptoms can be managed. Rosacea can triggered by different things in different patients, so treatment differs accordingly. The doctor may prescribe drugs, such as:
- antibiotics and tetracycline derivatives;
- topical preparations, or;
- laser or intense pulsed light therapies.

















