Sleep apnoea
Mr Asit Arora - Otolaryngology / ENT
Created on: 10-28-2015
Updated on: 11-10-2023
Edited by: Carlota Pano
What is sleep apnoea?
Sleep apnoea is the interruption of breathing that occurs when you are asleep. The most common type of sleep apnoea is known as obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA).
Obstruction of breathing causes a drop in oxygen levels in the body, which makes it difficult for the patient to have a restful night of sleep and will, therefore, show signs of tiredness the next day. In addition, the lack of oxygen intake can lead to hypertension and future heart failure, so it is advisable to detect it early and seek treatment.
The main types of sleep apnoea are:
- Obstructive sleep apnoea: The most common, and it occurs when the mouth, nose and throat muscles relax.
- Central sleep apnoea: Occurs when the brain does not send the correct signals to the muscles that control breathing.
- Complex sleep apnoea: Occurs when someone suffers from central sleep apnoea and obstructive sleep apnoea.

Prognosis
Sleep apnoea can lead to serious health problems if it is not treated properly, and is linked with the following:
- high blood pressure
- heart failure
- cardiovascular disease
- stroke
- depression
- Other problems caused by having a lack of restful sleep (e.g. trouble concentrating at work, and an increased chance of road traffic accidents)
It is essential to go to a specialist to receive adequate treatment.
Sleep apnoea symptoms
The symptoms can be the same with central apnoea and obstructive apnoea. The main symptoms are:
- breathing stopping and starting
- gasping and snorting as breathing is disrupted
- snoring loudly
- waking up frequently
- waking up with a sore throat or dry mouth
- daytime sleepiness (hypersomnia)
- irritability
- attention problems
Medical tests for sleep apnoea
Early detection of sleep apnoea is important. Therefore, a sleep study is required to confirm a diagnosis and to establish a treatment plan. The sleep specialist will do an assessment that may involve monitoring your breathing and other bodily functions whilst you are asleep.
Tests to detect sleep apnoea may include the following:
- Nocturnal polysomnography: This test assesses the activity of the lungs, brain and heart, movement of legs and arms, breathing patterns and, finally, blood oxygen levels while the patient sleeps.
- Sleep tests at home: These are simple tests to diagnose sleep apnoea at home. Pulse, blood oxygen level, airflow, and breathing patterns are usually measured.
For obstructive sleep apnoea, an otolaryngologist is usually referred, who may rule out a blockage in the throat or nose. A cardiologist or neurologist can also look for the causes of central sleep apnoea.
What are the causes of sleep apnoea?
Obstructive sleep apnoea occurs when the muscles in the back of the throat relax. As soon as they relax, the airways narrow, preventing proper inhalation, which reduces the level of oxygen in the blood.
Central sleep apnoea occurs when the brain does not transmit the right signals to the breathing muscles. This results, for a short period of time, in the patient not breathing, causing them to awaken with shortness of breath and with difficulties in falling asleep again.
Can sleep apnoea be prevented?
Sleep apnoea cannot be definitively prevented, but there are some guidelines that can be followed to decrease the risk:
- Lose weight or maintain a healthy weight
- Exercise regularly
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Eat a healthy, balanced diet
- Avoid taking sleeping medications, unless advised by a doctor
Treatments for sleep apnoea
The specialist will determine the treatment plan. Some dental devices can be used as a treatment for mild cases of obstructive sleep apnoea. These devices facilitate breathing by moving the jaw forward.
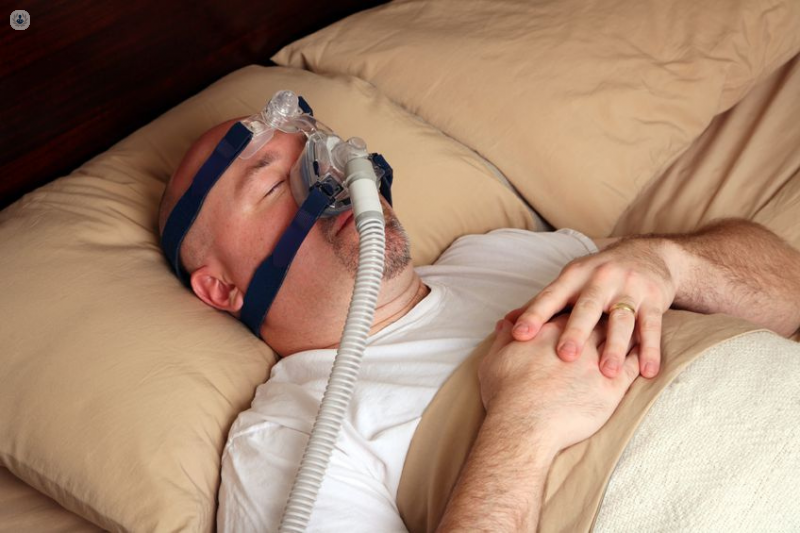
A common treatment for sleep apnoea is CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure). It consists of placing, during sleep, a special mask over the mouth and nose. This mask keeps the airways open by adding pressure to the air the patient breathes in.
In less frequent cases, surgery may be required to remove the tonsils or extra tissue from the throat.
Which specialist treats you?
A multidisciplinary team of specialists can participate in the treatment of sleep apnoea, among which we can find specialists in otorhinolaryngology, pulmonology, cardiology and endocrinology.