Dental pain
Professor Federico Foschi - Endodontics
Created on: 10-11-2017
Updated on: 12-19-2023
Edited by: Carlota Pano
What is dental pain?
Dental pain, or a toothache, is a pain in a tooth caused by the nerve in the root of the tooth becoming irritated. The central part of the tooth, known as the dental pulp (soft tissue part), becomes inflamed.
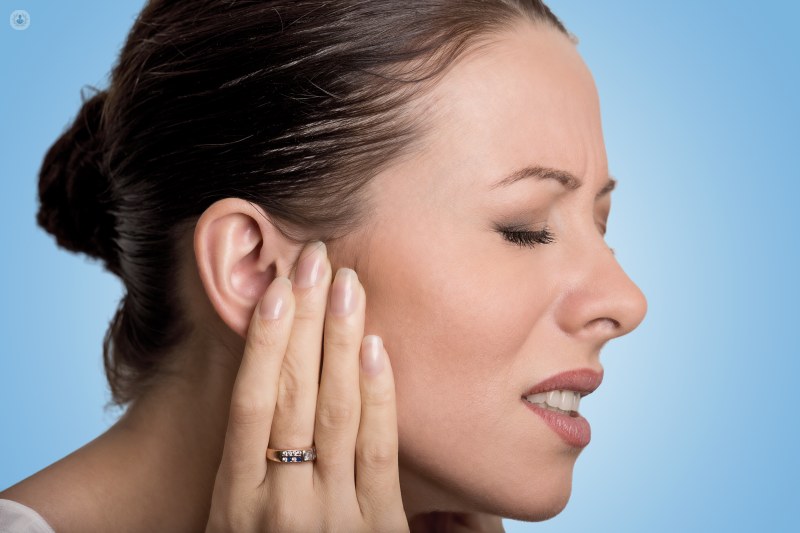
What are the symptoms of dental pain?
Common symptoms in relation to dental pain are:
-
A constant toothache
-
Pain when eating or drinking something hot or cold (lingering in nature)
-
Disrupted sleep
-
Pain when chewing
-
Swollen jaw and face
-
Pain radiating to the ear and jaw
How is dental pain diagnosed?
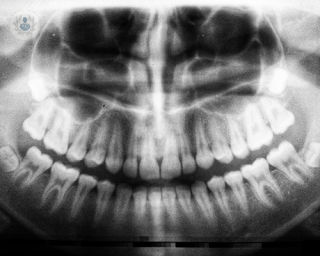
Dental pain can be diagnosed by a dentist or an endodontist. They may tap on the tooth to identify the source of the pain, look for areas of dental decay, swelling and redness. Cold may be applied to the affected tooth to replicate the response. Your dentist will need to ensure that the pain is caused by your teeth and not by sinusitis, an ear infection, or an injury to the temporomandibular joint.
A thorough medical history assessment and oral exam can lead to a diagnosis. X-rays are often used to get a clearer picture of the source of the pain.
What are the causes of dental pain?
The most common causes of a toothache are tooth decay, dental cavities, injury, or infection. Sometimes, pain originating from the jaw joint (temporomandibular disorder), the ears, or the sinuses can cause what feels like a toothache.
Can dental pain be prevented?
Most dental problems can be avoided by:
-
Regularly brushing the teeth with fluoride toothpaste
-
Flossing and using mouthwash
-
Having your teeth checked and cleaned twice per year
How is dental pain treated?
Dental pain treatment will depend on the cause. The dentist will perform tooth fillings, or a tooth extraction, or a root canal treatment as required, depending on the situation.
Antibiotics will normally be prescribed only if there is fever or swelling present. Otherwise, with an endodontic infection, the only way to eradicate the bacteria is to either extract the tooth or carry out root canal treatment.
If dental pain is the result of something other than the teeth or jaw, then management will depend on the condition.