Nephropathy (Kidney disease)
Professor Liz Lightstone - Nephrology
Created on: 12-17-2015
Updated on: 06-09-2023
Edited by: Aoife Maguire

What is nephropathy?
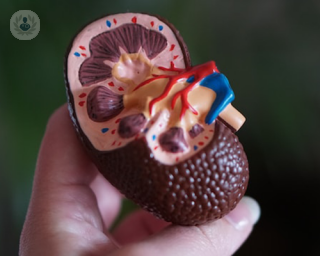
Nephropathy, also known as kidney disease, is any damage or disease to the kidneys. Nephropathy usually causes a loss of kidney function. If enough damage has occurred, you are considered to have kidney failure, a potentially fatal condition where the patient will need dialysis or a kidney transplant to replace the function of their kidneys.
Kidney disease can be classed as nephritis (inflammatory kidney disease) or nephrosis (non-inflammatory kidney disease). It can also be classed as acute (damage occurs over a very short period of time or is related to a single event) or chronic (damage compounds gradually over time).
Diabetic nephropathy
Diabetic nephropathy is damage to the kidneys as a result of type 1 or type 2 diabetes. Consistently high blood sugar levels damage the filtration system of the kidneys over time, with symptoms such as:
- protein in the urine
- loss of appetite
- increased need to urinate
- nausea
- fatigue
Diabetic nephropathy can be prevented by keeping your blood sugar levels under control, which can mean diet control and appropriate insulin intake if you have diabetes. Similarly, treatment involves managing your blood sugar levels as well as your blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
IgA nephropathy
IgA nephropathy, also known as “Berger’s disease”, occurs when the antibody immunoglobulin A is released by your body and gets stuck in the kidneys, causing inflammation. This can cause your kidneys to leak protein as well as blood, which appear in the urine. However, at first you may not notice any symptoms at all and you can have the disease for decades without noticing.
The exact cause of IgA nephropathy is unknown but it is thought to be related to your genes and certain conditions such as infections, coeliac, and liver diseases. It can be treated with steroids, immunosuppressive drugs, ACE inhibitors, and dietary changes.
Hypertensive kidney disease
High blood pressure is one of the leading causes of kidney disease and kidney failure. High blood pressure can lead the arteries around the kidneys to narrow or harden, weakening the blood supply to the kidneys. This leaves the kidneys starved of the nutrients they need, reducing their ability to filter blood and fluids in the body. In turn, the kidneys are unable to release a hormone that helps to regulate blood pressure, and the problem gets worse.
The main treatment for hypertensive kidney disease is medication such as ACE inhibitors and ARB drugs, which act by reducing your blood pressure.
Analgesic nephropathy
Analgesic nephropathy is kidney damage caused by taking painkillers such as aspirin and ibuprofen. These are usually harmless to the kidneys but can cause damage if taken in combination over a long period of time, or if you have an existing condition such as lupus, cirrhosis or heart failure. You are more likely to suffer from analgesic nephropathy if you combine analgesics with caffeine or codeine.