What happens during an ECG?
Escrito por:In this article below, distinguished consultant cardiologist, Dr Anna Marciniak, shares her expert insights with regards to electrocardiograms.
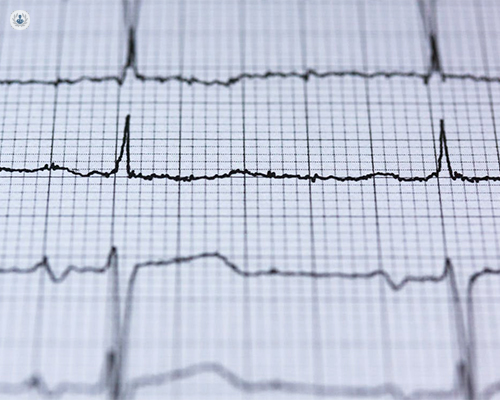
What is an electrocardiogram?
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a non-invasive diagnostic test that provides valuable information about the electrical activity of the heart. This simple and painless procedure involves attaching electrodes to the skin to record the heart's electrical impulses, which are then displayed as waves on a monitor or printed on paper. ECGs are widely used by healthcare professionals to detect and diagnose various heart conditions, assess cardiac function, and monitor treatment effectiveness.
Why are ECGs performed?
The primary purpose of an electrocardiogram is to evaluate the heart's rhythm and electrical conduction system. By measuring the timing and strength of each heartbeat, an ECG can detect abnormalities such as arrhythmias (irregular heart rhythms), conduction disorders, and signs of ischemia (reduced blood flow to the heart muscle).
These findings can provide valuable insights into the presence, severity, and nature of cardiovascular conditions, helping healthcare providers make informed decisions about patient care.
What happens during an ECG?
During an ECG, electrodes are placed on specific locations on the chest, arms, and legs to capture the heart's electrical signals from different angles. The resulting waveform patterns, known as P waves, QRS complexes, and T waves, reflect the various phases of the cardiac cycle and can indicate normal cardiac function or abnormalities. For example, changes in the ST segment or T wave morphology may suggest myocardial ischemia or infarction, while irregularities in the PR interval or QRS duration may indicate conduction abnormalities or arrhythmias.
What are the advantages of ECGs?
ECGs are used in a variety of clinical settings, from routine screenings and preoperative evaluations to emergency assessments and ongoing monitoring of patients with known heart conditions. In addition to diagnosing heart disease, ECGs can help evaluate the effectiveness of medications, monitor the progression of cardiac disorders, and guide treatment decisions such as the need for pacemaker placement or cardiac catheterisation.
Another advantage of ECGs is their accessibility and simplicity. The test can be performed quickly and easily in a physician's office, hospital, or clinic, requiring minimal preparation or patient discomfort. Moreover, advances in technology have made portable ECG devices available for home use, allowing patients to monitor their heart rhythm and share data with healthcare providers remotely.
If you wish to consult with Dr Anna Marciniak, simply visit her Top Doctors profile today.


