Nephrocalcinosis
What is nephrocalcinosis?
Nephrocalcinosis is a kidney disorder in which an excess of calcium is deposited in the kidneys. It is common in premature babies and in most cases, both kidneys are affected. Nephrocalcinosis is related to kidney stones (nephrolithiasis), although it is not the same disease.
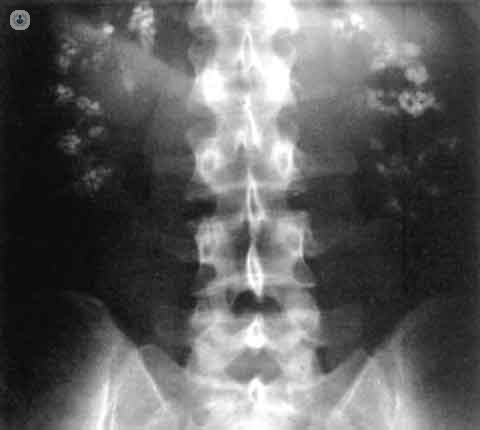
What are the symptoms of nephrocalcinosis?
In many cases nephrocalcinosis does not cause any early symptoms. However, people who, in addition to nephrocalcinosis, suffer from symptoms of an underlying condition kidney stones may have:
- blood in the urine
- fever and chills
- nausea and vomiting
- abdominal pain
- pain in both sides of the back, in the groin or testicles
- pain in the groin or testicles
In addition, late symptoms of nephrocalcinosis may be associated with chronic renal failure.
Causes of nephrocalcinosis
Nephrocalcinosis can be caused by a number of disorders that cause elevated calcium levels in the blood. Examples include:
- alport syndrome
- bartter syndrome
- chronic glomerulonephritis
- family hypomagnesaemia
- medullary spongy kidney
- primary hyperoxalurias
- rejection of a kidney transplant
- renal tubular acidosis (RTA)
- renal cortical necrosis
In addition, other causes include:
- ethylene glycol toxicity
- hypercalcaemia (excess calcium in the blood) due to hyperparathyroidism
- use of medications such as acetazolamide, amphotericin B and triamterene
- sarcoidosis
- kidney tuberculosis or AIDS-related conditions
- vitamin D toxicity
Can nephrocalcinosis be prevented?
Nephrocalcinosis can only be prevented by correctly treating those disorders related to high levels of calcium in the kidney. If these conditions are treated early, they can help prevent nephrocalcinosis.
What is the treatment for nephrocalcinosis?
Nephrocalcinosis treatment aims to reduce the symptoms and prevent more calcium from building up in the kidneys. In this way, it will include methods to reduce the levels of calcium, phosphate and oxalate in the blood and urine.
These methods include changing the diet or taking certain medications and vitamin supplements. Treatment will also be directed at the underlying condition that is causing nephrocalcinosis.
What specialist treats this condition?
Nephrologists generally treat all kidney-related medical conditions.
