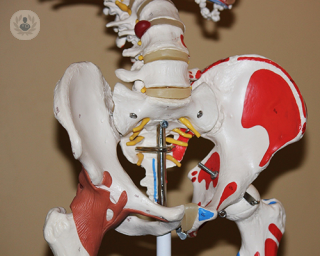
Hip replacement
Professor Lee Jeys - Orthopaedic surgery
Created on: 11-29-2013
Updated on: 09-20-2023
Edited by: Kate Forristal
What is a hip replacement?
A hip replacement is a type of surgery in which a degenerated hip is replaced with an artificial joint.
There are different kinds of hip prosthesis which depend on how the affected bones are replaced:
- total hip replacement
- revision prosthesis
- hip resurfacing
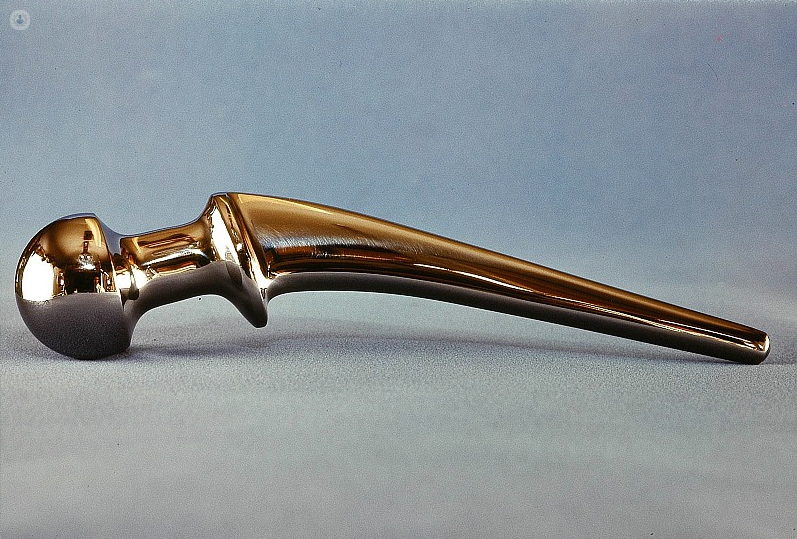
Why would you do it?
A hip replacement is used to alleviate pain and restore function in patients who have not responded to previous treatment (rest, rehabilitation, and anti-inflammatories).
Replacing the hip with a prosthesis is recommended in cases where there is hip osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, or a hip fracture.
What does it involve?
To carry out the procedure general or spinal (from the waist down) anaesthetic is used. When replacing the prosthesis, general anaesthetic is used as the procedure tends to take more time.
The materials used in a hip prosthesis are intended to make movement be as similar as possible to normal joint movements. Different types of metal are used to make the implants, including: stainless steel, cobalt alloys, chromium, titanium. Some replacements are made of plastic – normally polyethylene, which is highly durable and resistant to wear and tear.
The surgery usually takes between 60 and 90 minutes to complete.
How to prepare for a replacement
A preoperative study is carried out before the procedure and includes:
- blood tests
- chest X-ray
- echocardiogram
In some cases, additional tests may be needed, such as a pulmonary ventilation test or allergy tests.
Finally, you will have a meeting with the anaesthetist to check your suitability for a general anaesthetic or epidural.
Post-operative care
After the operation, you are likely to need to use crutches for four to six weeks. Rehabilitation is a long process but you will be enrolled in a program to help you get moving again and gradually build up your strength.
To help the area recover:
- wash the surgical wound and gently massage in moisturiser twice a day
- keep the leg elevated whenever possible
- sit on chairs that are high and have armrests or sit on firm sofas.
- use comfortable shoes that give good foot support
- follow a balanced diet that is high in iron and fibre and with plenty of fluids
- take extra care at home, removing carpets, cable, or furniture that could cause a fall and be careful on wet floors
It can also help to sleep face up and with a pillow between the legs and not to sleep on their side. When going to the toilet, you can use a raise toilet seat temporarily to avoid excessive joint flexion.
Finally, it is important to seek urgent medical help if you experience the following symptoms:
- a heavy ache in the hip
- pain and tenderness in one of your legs
- breathlessness or chest pain
- a high temperature
- hip pain even at rest