Microscopic root canal treatment, does it always make sense?
Written by:Root canal treatment has been a common procedure for many years. Since technology and techniques have advanced in dentistry, it is now possible to ensure a faster, safer, and easier treatment process for patients. Expert specialist in prosthodontics Professor Christian Mehl has explained how having a root canal treatment with a microscope is done and what the benefits are in this article.
What is a root canal treatment?
Root canal treatment, also known as endodontic treatment, involves removing infected pulp (nerve) from the tooth’s root canals. It prevents the infection from spreading and can help save a tooth from having to be extracted.
The success rate of a root canal treatment is around 70 to 90 per cent in general. The complication of the root canal system at the end of the tooth plays a major role in the success of the treatment. With very fine root canals and complex ramifications, treatment often becomes challenging. A surgical microscope or dental loupes with a high magnification enables dentists to perform this highly intricate treatment with optimal accuracy.
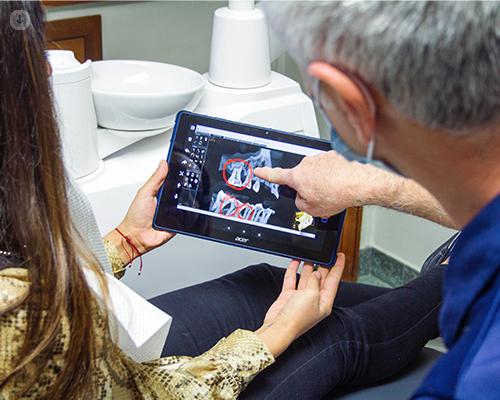
What is the treatment process with a microscope?
The infected pulp within in the root canal of the tooth requires to be removed. Otherwise, it can lead to several painful complications, including abscess formation. In addition, the inflammation can spread throughout the body.
To gain access to the root canal, the dentist will carefully drill into the biting surface of the tooth. The inside of the tooth will then be meticulously examined using a surgical microscope. The up to 25-fold magnification not only creates safety when removing the infected pulp, but also helps the dentist to search for other hidden root canals to enable maximum accuracy. The dentist will also use an electronic measuring device to determine the length and position of the root canals. Once the infected root canals are located, the dentist can remove the infected pulp with special files. After that, the root canals will be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected, then filled with a rubber-like and biologically-inert root filling. The rest of the tooth is filled with a composite filling to close the access cavity that was created.
Post treatment we typically give around 12 weeks for the root canal treatment to settle and ensure success before the affected tooth can be reconstructed with a partial or full crown.
What are the advantages of root canal treatment with the surgical microscope?
For optimal accuracy, our root canal treatments are routinely carried out with a surgical microscope or high magnification dental loupes. This significantly increases the success rate of a root canal treatment and ensures a safe delivery. With up to 25-times magnified vision and excellent illumination of the treatment area, the dentist can operate with optimal precision. The risk of overlooking any infected root canals as well as removing healthy tooth tissues is drastically reduced.
If you are having tooth ache or think you may need a root canal treatment, you can go to Professor Mehl's profile and book a consultation.


