Thrombophlebitis
What is thrombophlebitis?
Thrombophlebitis is the inflammation of a leg vein caused by a blood clot (thrombus). The vein can either be close the surface of the skin (superficial thrombophlebitis) or in a deep vein (deep vein thrombosis).
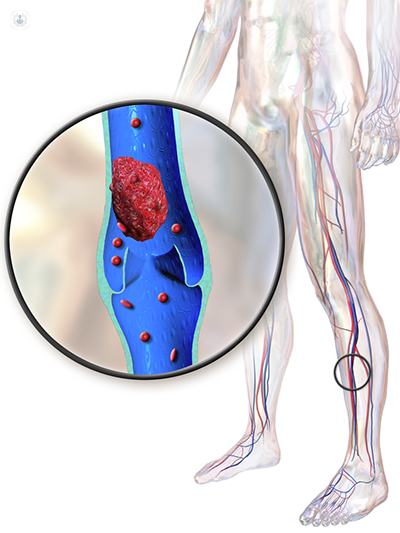
What are the symptoms of thrombophlebitis?
The symptoms of superficial thrombophlebitis are:
- Redness
- Swelling
- Tenderness and pain in the affected area
- Difficulty flexing your ankle
The symptoms of deep vein thrombosis are:
- Swelling
- Pain
What causes thrombophlebitis?
Thrombophlebitis is caused by a blood clot, which can be caused by:
- An injury to the vein
- Being sat down or immobile for long periods (e.g. if you are injured or in hospital)
- You have an inherited blood-clotting disorder
- Contraception (oestrogen) or hormone replacement therapy (HRT)
Varicose veins can also cause thrombophlebitis as they can stretch the blood vessels too much, allowing blood to pool which can lead to blood clots.
Can thrombophlebitis be prevented?
Preventing thrombophlebitis relies on the prevention of blood clots forming. The following measures can help prevent this:
- On long flights or car journeys, wear loose-fitting clothing and take regular breaks to stretch and walk your legs. Whilst seated it is good to flex your ankles up and down and stay hydrated.
- Stop smoking
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Eat a healthy diet, low in transgenic fats.
- If you have high cholesterol, take measures to reduce it.
How is thrombophlebitis treated?
The treatment will depend on the location, extent, symptoms and medical conditions of the patient. The main objective of the treatment is to mitigate pain and inflammation and prevent further thrombophlebitis from occurring in the future. Medicine to relieve swelling and pain may be given, and it is recommended that you elevate the leg. It is also recommended to apply a warm compress to the area for half an hour two to three times a day.
Additional treatment measures are:
- Compression stockings
- Varicose vein removal (a surgical procedure)
- Blood-thinning medication








