Indigestion (dyspepsia)
Dr Devinder Bansi - Gastroenterology
Created on: 11-13-2012
Updated on: 05-02-2023
Edited by: Lauren Dempsey
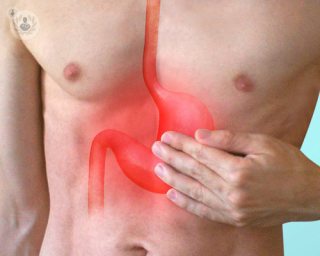
What is indigestion?
Indigestion, also medically referred to as dyspepsia, is a pain in the upper abdomen that occurs particularly after eating. It is normally a sign of an underlying problem.

How common is indigestion?
It’s a very common condition. Most people experience it during their lifetime, having mild and infrequent symptoms. It is particularly common during pregnancy, from week 27 onwards due to hormonal changes and the baby pressing on the stomach as it grows.
What is the main cause of indigestion?
There is uncertainty about the exact causes of dyspepsia. In some cases, the symptoms occur after a large meal or having taken medications that cause some damage to the gastric mucosa which is the lining of the stomach, specifically from taking too many aspirin or anti-inflammatory drugs. Some psychological problems such as stress, anxiety, or depression can be triggers. There are cases in which patients suffer an ulcer in the stomach in the area of the duodenum, mostly caused by a bacterium called Helicobacter pylori.
The most common causes of dyspepsia are:
- excessive alcohol consumption
- eating spicy or greasy foods
- eating large quantities of food in a short time frame
- smoking tobacco
- eating foods with high fibre content
- excessive consumption of caffeine
What are the symptoms of indigestion?
The most common symptom is discomfort in the upper abdomen, which usually manifests during or after meals. This pain can be described as a warm or burning sensation in the area between the navel and the lower part of the sternum.
Other symptoms include:
- bloating or feeling full
- nausea
- burping and farting
- regurgitating food or liquid that results in a bitter taste in the mouth
How long does indigestion last?
In mild cases, the symptoms of indigestion will typically last for a few hours. Over the following days, symptoms may reoccur but they will go away themselves or can be managed with adjustments to diet or lifestyle.
How do I relieve indigestion?
Normally, indigestion isn’t a sign of a serious condition and it can be self-managed. Things you can do to relieve the symptoms include:
- drink plenty of water
- stay upright and don’t lie down
- take over-the-counter medication to neutralise stomach acid
- have a warm bath
- chew sugar-free gum
- eat a ripe banana

When should you visit a doctor?
Although generally indigestion isn’t serious, you should seek medical attention if:
It occurs frequently over a period of two weeks
- it causes severe pain
- you're over the ag of 55
- you experienced unexplained weight loss
- you have dysphagia, difficulties when swallowing
- you often vomit
- you have anaemia
- you feel a lump in your abdomen
- you have blood in your stool or vomit
Which type of specialist treats indigestion?
Doctors who specialise in digestive diseases, such as gastroenterologists, treat indigestion.
How is indigestion diagnosed?
When diagnosing indigestion, specialists resort to two tests:
- Abdominal ultrasound. Ultrasound waves are used to visualise and study the abdomen.
- Gastrointestinal endoscopy. This examination is performed to obtain images of the oesophagus, stomach and duodenum to detect and identify if there are any injuries.
How is indigestion treated medically?
Indigestion can be alleviated by taking medication to reduce heartburn and protect the stomach. Typical medications include:
- antibiotics to treat bacterial infections
- H2 blockers that decrease the amount of acid that’s produced
- proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) which decrease acid in your stomach
How can indigestion be managed?
The discomfort felt from indigestion can be alleviated if healthy habits are acquired. These include:
- maintaining a healthy weight
- quit smoking
- avoid consuming spicy or fatty foods
- avoid drinking excess caffeine and alcohol
- don’t eat for 3-4 hours before going to bed
- avoid aspirin and ibuprofen
What is the prognosis of indigestion?
The prognosis of indigestion is most often positive and without major consequences. However, in many cases, it evolves into a chronic disease and may appear and disappear intermittently over the years. On rare occasions, it originates from a serious disease with a negative prognosis.
Can indigestion be prevented?
There are some habits that can help to prevent the condition such as avoid stress and exercise immediately after eating, and chew food well. In patients who have previously suffered episodes of indigestion, it’s advisable to avoid taking some medications such as acetylsalicylic acid and some anti-inflammatories on an empty stomach. Speak to your specialist for individual advice.
What complications can arise from indigestion?
Usually, there are no serious complications that arise from indigestion, but it can cause discomfort and impact your quality of life.