Sports cardiology
Dr Navin Chandra - Cardiology
Created on: 11-13-2012
Updated on: 11-08-2023
Edited by: Kate Forristal
What is sports cardiology?
Sports cardiology is a sub-specialty of cardiology that diagnoses and treats heart conditions in athletes and assesses if the patients are fit to participate in sports. It encompasses a series of tests aimed at identifying heart muscle diseases that may pose a risk when playing sport. These tests allow doctors to analyse the health of the heart and how well it copes with intense physical exercise.
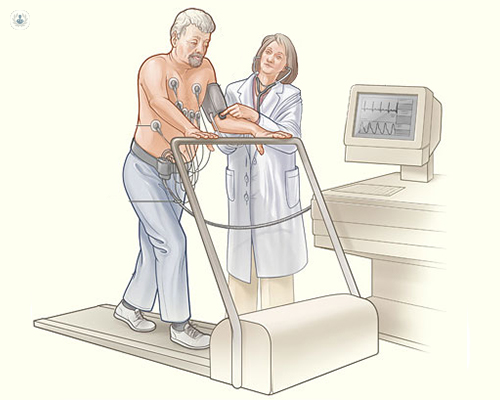
What does sports cardiology involve?
The patient may require a number of tests depending on their needs, medical history and the sport they practice. Common tests used in sports cardiology include:
- Electrocardiogram – this is a basic test to monitor heart rate using electrodes placed on the chest. It enables the detection of arrhythmias.
- Echocardiogram – this imaging test allows observation of the heart's activity by means of ultrasound and can pick up abnormalities that would otherwise have gone undetected on the electrocardiogram.
- Holter monitor test – this test measures your heart rate for several hours (up to 24 hours) while you go about your usual daily activity, and it shows the activities and times of the day in which your heart rate is particularly high or low.
- Stress test (ergospirometry) – the patient is asked to run on a treadmill or to pedal a stationary bicycle while their heart rate, blood pressure, and breathing are monitored. This data can be compared to data obtained while the patient is at rest to assess if there is a heart problem.
Why is sports cardiology necessary?
This series of tests is aimed at both professional and amateur athletes and people who are starting a new sporting activity.
Sport can push our body and heart to the limit, so it is essential to know how far we can go without damaging our health.
These tests are therefore aimed at preventing serious heart problems such as heart attacks, Brugada Syndrome or sudden death syndrome, and for monitoring people who have had heart surgery, or who suffer from heart failure, arrhythmias or congenital heart disease.
Thus, the aim of sports cardiology is to provide athletes with the necessary tests and advice to avoid health risks when practicing sport, as well as to assure people with illnesses such as heart disease that it is safe to continue to practice sport.
An annual sports cardiology check-up is recommended for all athletes, especially those with heart problems.
People with a heart condition who are planning to start a new sporting activity should also have a check up to find out in advance if it could harm their health.
Anybody who has symptoms such as arrhythmias, chest pain, dizziness, or shortness of breath during sports should see a sports cardiologist find out the cause.
Preparing for sports cardiology tests
These tests are minimally invasive and require no special preparation.
The cardiologist may advise you on what clothes to wear or what food and drink you can have before the tests, as drinks such as coffee and tea, which contain stimulants are often discouraged so as not to affect the results.
What do you feel during the tests?
Sports cardiology tests are minimally invasive procedures and are not painful.
In the case of stress tests, however, you will have to exert yourself physically, so you may feel tired or even dizzy and have difficulty breathing.
Meaning of abnormal results
Abnormal results from sports cardiology tests may mean that you have a heart condition and can no longer play certain sports, or at least not at high intensity.
The cardiologist will evaluate the results and may ask that you repeat a test or have further tests to confirm the diagnosis.

















